TUI Flight Delay Compensation: The Passenger’s Handbook
August 25, 2023Monitor your sales and success every day for better results
August 26, 2023
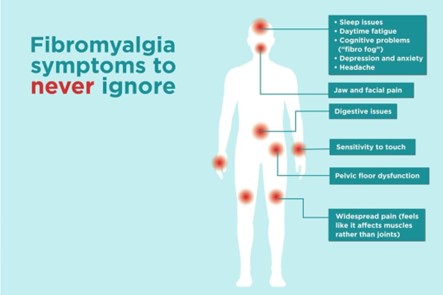
Fibromyalgia is the third most frequent musculoskeletal condition characterized by fatigue, sleep disturbances, and other cognitive and somatic symptoms. This condition is believed to be associated with central pain processing that heightens painful and non-painful stimuli responses.
Due to the complexity of the disorder, the etiology of fibromyalgia is still unknown. However, stem cell therapy offers new hope for managing symptoms, promoting rapid healing, and replacing damaged cells with healthy ones.
Let’s take a deeper look at other fibromyalgia nontraditional treatment options, their limitations, and the role of stem cell therapy in managing symptoms effectively.
The limitations of traditional fibromyalgia treatment
Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder triggered by either physical trauma, surgery, infection, or psychological experience. For decades, fibromyalgia wasn’t even considered a legitimate illness; therefore, no treatment cure or targeted interventions were discovered. Due to a lack of knowledge, traditional fibromyalgia treatment options have certain limitations in their therapeutic effects, such as:
Symptomatic relief
Most treatments offer symptom management rather than treating the disorder’s underlying cause. Some commonly prescribed medications include:
- Antidepressants
- Pain killers
- Anti-seizure drugs
Limited knowledge
Due to a lack of knowledge, the disorder remains incurable, which is why most treatments are generalized and lack a targeted approach for treating symptoms.
Side effects and addiction
Most patients experience side effects from prescriptions like drowsiness, dizziness, gastrointestinal issues, etc., impacting a person’s quality of life. Some medications, like opioids, can lead to addiction if used long-term.
Treatment costs
Most fibromyalgia nontraditional treatment interventions, such as stem cell therapy, are inaccessible to patients due to the costs involved.
Trial and error approach
Due to insufficient supporting evidence, the disorder is mostly treated via a trial-and-error approach to find the most effective targeted treatment for the patient.
How stem cell therapy can help alleviate fibromyalgia symptoms?
Stem cell therapy as a regenerative medicine helps alleviate fibromyalgia symptoms. They do so by repairing and regenerating tissues within the body.
Stem cells can differentiate into specialized cells, self-renew, and have anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties. These cells potentially reduce inflammation, modulate the immune response, and promote the regeneration of cells in damaged tissues.
Stem cell for fibromyalgia has been found to alleviate:
- Muscle and joint stiffness.
- Tenderness.
- Chronic body pain.
- Fatigue.
- Tingling within arms and legs.
- Deterioration in focus and memory.
- Sensitivity to light, noise, odors, and temperatures.
- Digestive issues, such as constipation and bloating.
Types of stem cell therapy for fibromyalgia
Depending upon each therapy’s considerations and approaches, cell-based therapy for fibromyalgia uses different types of stem cells, for instance:
Mesenchymal stem cells
MSCs are adult stem cells with the potential to reduce inflammation and modulate the immune response associated with the disorder.
Hematopoietic stem cell
Hematopoietic stem cells have the unique characteristics to produce blood cells. They’ve also shown promise in treating autoimmune and inflammatory disorders like fibromyalgia.
Adipose-derived stem cell
Adipose tissues are a rich source of mesenchymal stem cells and have been used to initiate tissue repair and treat inflammation in fibromyalgia.
Safety and efficacy of stem cell therapy
Stem cell therapy is currently the most promising therapeutic approach for treating various diseases. However, the safety and efficacy of the treatment depend entirely upon the health condition of the patient, and the type of stem cell therapy being used.
Safety
- Stem cell therapy is medically safe when it uses adult stem cells — the patient’s own or, sometimes, sourced from a donor.
- The source of cells, their type, and processing methods greatly affect the safety of a procedure.
- Illegitimate clinics and running unregulated treatments can do significant harm to patients.

Effectiveness
- According to clinical trials and research, stem cell therapy is often effective in musculoskeletal and neurological disorders, including fibromyalgia, as well as in certain autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
- The efficacy of stem cell therapy largely depends upon the factors like stage of the disease, the type of stem cells being used, the delivery method, and individual patient characteristics.
The future of stem cell research for fibromyalgia
Some potential avenues that stem cell research can help include:
Understanding disease
Understanding the disorder and its underlying mechanisms to develop and progress targeted treatments for hard-to-treat diseases.
Regenerative medicine approach
This provides the regeneration of damaged or injured tissues in fibromyalgia patients. For instance, mesenchymal cells have been proven for their anti-inflammatory and tissue repair properties, making them a candidate for treating fibromyalgia.
Personalized medicines
Stem cell research can help identify the treatment response of a patient and develop targeted treatment plans for individuals.
Drug discovery
Stem cells can also help screen and discover new drugs for treating fibromyalgia, specifically targeting symptoms while addressing the disease process.
In conclusion
Fibromyalgia is a complex disorder with unknown pathology and biomarkers. Most traditional treatment avenues are unable to manage fibromyalgia symptoms effectively or may cause side effects. Stem cell therapy, however, offers potential future directions for understanding and treating the underlying causes of the condition. Although the efficacy of the treatment may vary from person to person, stem cells have shown great improvements in patients experiencing symptoms of fibromyalgia such as chronic pain and discomfort.

